What is in the Trigonum Vesicae located?
the bladderA triangular smooth area at the base of the bladder between the openings of the two ureters and that of the urethra.
What is trigonum vesicæ?
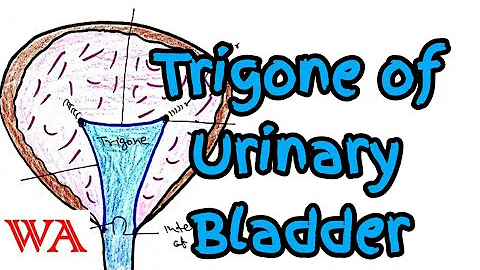
The trigone (a.k.a. vesical trigone) is a smooth triangular region of the internal urinary bladder formed by the two ureteric orifices and the internal urethral orifice.
What structures are present in the trigone of the bladder?
The bladder trigone is a triangular shaped region at the base of the bladder defined by the two ureteral orifices and the internal urethral meatus.
What is the trigone and where is it located?
There is a triangular area, called the trigone, formed by three openings in the floor of the urinary bladder. Two of the openings are from the ureters and form the base of the trigone.
What is the trigone made of?
The trigone is formed predominantly from bladder muscle. Histological studies suggest that two muscle groups reside in the trigonal region: the detrusor muscle of the bladder and longitudinal ureteral fibers.
What is the other name of Trigonum Vesicae?
A triangular smooth area at the base of the bladder between the openings of the two ureters and that of the urethra. Synonym: trigonum vesicae, lieutaud's body, lieutaud's triangle, lieutaud's trigone, vesical triangle.
Where is the Trigonum located?
What Is the Os Trigonum? The os trigonum is an extra (accessory) bone that sometimes develops behind the ankle bone (talus). It is connected to the talus by a fibrous band. The presence of an os trigonum in one or both feet is congenital (present at birth).
What three structures make up the trigone?
The three structures that outline the triangular region of the bladder known as the trigone are the two openings of the ureters (on the left and right side) as well as the inner urethral orifice.
What three structures are connected by the trigone?
Urinary Bladder, Ureter, and Urethra
The urothelium of the trigone and the musculature and other connective tissue components of the bladder and urethral walls are of mesodermal origin. The ureters are derived entirely from mesoderm.
What is the anatomy of the trigone?
Trigone. The trigone is a triangular portion of the bladder floor bordered (ventrally) by the internal urethral opening or bladder neck and (dorsolaterally) by the orifices of the right ureter and left ureter.
What 3 structures are connected by the trigone?
Urinary Bladder, Ureter, and Urethra
The urothelium of the trigone and the musculature and other connective tissue components of the bladder and urethral walls are of mesodermal origin. The ureters are derived entirely from mesoderm.
Where is the uvula Vesicae located?
A slight projection into the cavity of the bladder, usually more prominent in old men, just behind the urethral opening, marking the location of the middle lobe of the prostate.
What ligaments are in the os trigonum?
The os trigonum is related directly to the flexor hallucis longus (FHL) and KFP. The posterior part of the talofibular ligament inserts on the os trigonum [8]. Other ligaments of the posterior process of the talus occur variably [27].
What does Trigonum mean?
a Latin word meaning "three-sided", used in medical names and descriptions: the os trigonum.
What is the trigone bounded by?
carotid trigone the triangular area bounded by the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and the anterior midline of the neck.
What is the importance of Trigonum Vesicae?
The trigone (a.k.a. vesical trigone) is a smooth triangular region of the internal urinary bladder formed by the two ureteric orifices and the internal urethral orifice. The area is very sensitive to expansion and once stretched to a certain degree, the urinary bladder signals the brain of its need to empty.
What is uvula vesicae?
uvula ves·i·cae -ˈves-ə-ˌkē : an elevation of the mucous membrane lining the lower anterior part of the bladder.
Which lobe of prostate forms uvula vesicae?
- The median lobe, which arises from the peri-urethral zone [4], is situated between the urethra and ejaculatory ducts. Its upper surface is bound by the bladder trigone and projects into the bladder producing the uvula vesicae, i.e., the elevation behind the internal urethral orifice.
What structures are involved in os trigonum?
What Is the Os Trigonum? The os trigonum is an extra (accessory) bone that sometimes develops behind the ankle bone (talus). It is connected to the talus by a fibrous band. The presence of an os trigonum in one or both feet is congenital (present at birth).
What are the 4 main ligaments of the ankle?
- Major ligaments of the ankle
- Anterior tibiotalar ligament (ATTL)
- Posterior tibiotalar ligament (PTTL)
- Tibiocalcaneal ligament (TCL)
- Tibionavicular ligament (TNL)
How big is the os trigonum?
The os trigonum is usually seen as an individual bone, but can also exist of two or more pieces. It is less than 1cm in size, but this can vary. The os trigonum is usually triangular with an anterior, inferior and posterior surface. The anterior surface connects with the lateral tubercle by cartilaginous synchondrosis.
What is the trigone and why is it important clinically?
The trigone is the neck of the bladder. It's a triangular piece of tissue located in the lower part of your bladder. It's near the opening of your urethra, the duct that carries urine from your bladder outside of your body. When this area becomes inflamed, it's known as trigonitis.
What is placed at the apex of the Trigonum Vesicæ in the most dependent part of the bladder and is usually somewhat Crescentic in form?
The internal urethral orifice
The internal urethral orifice is placed at the apex of the trigonum vesicæ, in the most dependent part of the bladder, and is usually somewhat crescentic in form; the mucous membrane immediately behind it presents a slight elevation, the uvula vesicæ, caused by the middle lobe of the prostate.
Where is the uvula vesicae located?
A slight projection into the cavity of the bladder, usually more prominent in old men, just behind the urethral opening, marking the location of the middle lobe of the prostate.
What process is the os trigonum?
The os trigonum (plural: os trigona) is one of the ossicles of the foot and can be mistaken for a fracture. It sits posterior to the talus on the lateral foot radiograph and represents a failure of fusion of the lateral tubercle of the posterior process. It is estimated to be present in ~7% of adults 1.
What is the pathology of os trigonum?
The os trigonum syndrome refers to symptoms produced by pathology of the lateral tubercle of the posterior talar process. Pain can be caused by disruption of the cartilaginous synchondrosis between the os trigonum and the lateral talar tubercle as a result of repetitive microtrauma and chronic inflammation.
